What are commodity codes?
Commodity codes are used to classify goods for import and export within the European Union (EU) or outside. The aim of classification is to pay the right tax and duty and follow regulations. If you want to move goods you must have a commodity code for all goods you want to import or export to and from the UK.
How it works
Goods are classified according to a system of ‘Commodity Codes’ which are used across the European Union (EU). Commodity Codes are composed of ten digit numbers, however for certain goods there are an additional four digits. The ten digits are used for imports from outside the European Union and it is needed for TARIC imports declaration. For exports from the UK you only need the first eight digit code. The latter code is used for export declarations and Intrastat commodity codes declarations (a system for collecting statistics on the trade in goods between EU member states).
Why Commodity Codes classification is important
Commodity codes are important in determining how the goods will be treated in the UK, the European Union and third countries. The classification of goods is essential in order to identify what duties and controls are applied and to ensure a correct customs declaration. You have the legal responsibility to ensure your goods are correctly classified, even if you have an agent who handles it on your behalf. Depending on how your goods are classified will affect how much will be charged for Duty, VAT, Quotas, Preferences, Suspensions, Common Agricultural Policy, excise and Intrastat.
Classifying your goods correctly ensure that:
- The amount you pay for duty and VAT is the correct amount.
- If there is any duty suspended to be applied to your goods.
- If there is any preferential duty rates to be applied.
- If you need an import or export license for specific goods.
- Whether excise or anti-dumping duties are applied.
- You do not pay the wrong interests on back-payments.
- Your goods are not seized or delayed.
The UK Trade Tariff is based on the EU TARIC and is daily updated from the TARIC so that importers or exporters can access accurate information.
You can use the online Trade Tariff to search for commodity codes on the gov.uk website. https://www.gov.uk/trade-tariff/sections
The TARIC
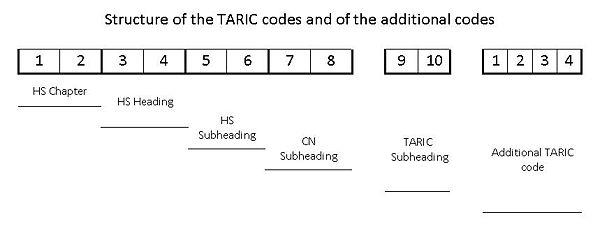
The TARIC code (Integrated Tariff of the European Communities) contents commodity tariff codes for member states of the EU and the rules applied to specific products when importing into EU or exporting goods from the EU. This includes the provisions of the Harmonised System (HS) and the combined nomenclature but also additional provisions specified in Community legislation such as tariff suspensions, tariff quotas and tariff preferences, which exist for the majority of the Community’s trading partners. The TARIC code is used by the customs to declare goods and calculate duties as well as for statistical declaration.
Classifications of goods are composed of the heading numbers. The first six digits are built upon the Harmonised System and they specify the product. Within the HS digit, the first two digits are known as the chapter numbers (HS chapter), which is the name for the chapter of the Trade Tariff. For example chapter 1 is Live Animals and chapter 2 is Meat and Edible Meat Offal. After the six HS digits, the next two digits are the Combined Nomenclature (CN) Subheading. If more details are required, there are an Additional TARIC code of four numbers.
For example Cocoa and Cocoa preparations will be classified as:
| HS Chapter | 2 digits | E.g. 18 – Cocoa and Cocoa Preparations |
| HS Heading | 2 digits | E.g. 1806 – Chocolate and other food preparations containing cocoa |
| HS SubHeading | 2 digits | E.g. 1806 10 – Cocoa powder, containing added sugar or other sweetening matter |
| CN SubHeading | 2 digits | E.g. 1806 10 15 – Containing no sucrose or containing less than 5% by weight of sucrose (including invert sugar expressed as sucrose) or isoglucose expressed as sucrose |
| TARIC Sub Heading | 2 digits | E.g. 1806 10 15 00 |